What is Port 514?
by Colin Cohen | Published on October 20, 2023

Port 514 is the default port for systems logs. Devices send system log messages to it for storage or analysis, which administrators can access easily.
Understanding Syslog Services
Syslog is an industry standard for system logging defined by RFC 5424 that is available on most Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux. While Windows systems don’t support syslog natively, it is possible to implement syslog clients and servers within it.
Syslog Messages Get Sent By Port Number 514
Syslog consists of a server that listens for logging messages on port 514 and a set of clients that send the logging messages to the server over this port. Implementing syslog allows you to store logs from various systems in a central location and the same format. With this data, you can then systematically manage and act upon this information.
Each message sent from a syslog client to the syslog server includes a facility code and a severity level, both of which have been long standardized.
The facility code denotes the system that is generating the log data. For example, code 0 is for kernel messages. Keep in mind: while these codes have been standardized, not all implementations of syslog map codes in the same exact way. There are also custom codes (16-22), which you can define any way you’d like for your specific purposes.
The severity level indicates the seriousness of the issue that the system is logging. For example, severity level 0, the highest severity, indicates an emergency, while severity level 7 (the lowest severity) indicates a message generated only for debugging. Be aware that individual implementations can define what constitutes a particular severity and act based on this in any manner they wish.
Devices and Software That Use Port 514
Many devices, such as routers and printers, use syslog over UDP port 514. Many software tools monitor and manage syslog data, such as Kiwi.
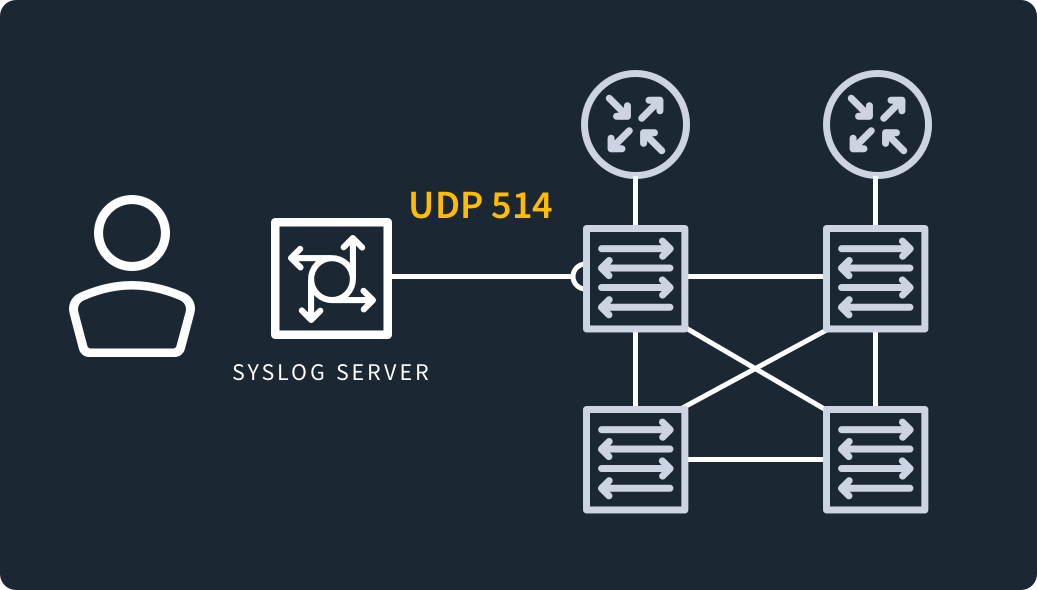
What Do You Use Syslog Port 514 For?
Port 514 is a well-known UDP port for syslog services.
Syslog works by sending standardized messages from syslog clients to a syslog server over port 514.
An Overview of How Port 514 Works
Each syslog message includes a header, which has the following fields:
Priority (a combination of the facility code and the severity level)
Version
Timestamp
Hostname
Application
Process ID
Message ID
Following the header, you may include structured metadata using key-value pairs, and then comes the message itself, which you should UTF-8 encode. The message consists of a TAG field, which represents the program or process that initiated the message, and a CONTENT field, which represents the message details.
A command-line utility, typically called logger, lets you send messages from a syslog client to the syslog server. You can view log files on the syslog server using a text editor such as vi or display them in the terminal using a command such as tail or less. You can search through the logs as well by using grep.
What Happens if Port 514 Is Configured Open?
You can configure port 514 to allow or block syslog transfers through your firewall settings.
Syslog Default Port Security Vulnerabilities
As the default syslog port, UDP port 514 can pose security vulnerabilities as attackers often target default ports for unauthorized access and data interception. You'll need to understand these risks so that you can take proactive measures to secure your syslog services.
How to Protect Sensitive Info in System Logs Through Port 514
Here are two ways to be proactive about protecting syslogs from data breaches.
Make the log files append-only
Filter sensitive information in system logs
Attackers often leave evidence of their activities in the logs that syslog has generated. So it's not unusual for them to try to delete the logs to cover their trail. But you can protect these logs from tampering by making the log files append-only. Do this in Linux through the following command:
chattr +a [filename]
In Linux, you can further disable an attacker’s ability to remove an append-only attribute placed on a file.
Another potential security issue with syslog is that sensitive information may intentionally or unintentionally appear in the logs, which could lead to serious data breaches if exposed. To avoid this, consider filtering out sensitive information in your logs, or encrypting it.
Is Syslog Port 514 a UDP or TCP Port?
Syslog 514 uses a connectionless, fast, and lightweight protocol known as UDP.
When you implement syslog over port 514, the protocol uses User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for transmissions. This provides for connectionless, fast, and lightweight logging.
However, UDP transport lacks congestion control mechanisms. It also doesn’t have authentication, and data loss is possible when using it. If any of these limitations are issues for you, you can implement secure syslog over port 6514, which uses TCP for transmissions. Using this further lets you use SSL/TLS to encrypt messages before they are sent across the network.
RELATED: Understanding UDP and TCP Transport Layer Protocols
Can Port 514 Have Port Conflicts?
At times, you may run into the issue of not being able to bind port 514 to your syslog server. This is likely because port 514 has already been bound to another application. To discover what application is bound port 514, you can run the following command from your terminal:
netstat -aon
The output of this command will indicate the process bound to port 514, which you will need to stop before you can properly start your syslog server.
It's also possible that you could face interference from firewall rules when using port 514. Depending on how your firewall rules are configured, you may also have to add a rule to allow traffic to your syslog server specifically.
Key Takeaways About Port 514
Implementing syslog over port 514 allows you to quickly and effectively generate and manage your system logs. The syslog protocol is an industry standard for system logging, commonly found on Unix-like systems, with servers listening for logging messages and clients sending data to the server over this port. This centralized log collection system allows for consistent management and action based on standardized facility codes and severity levels.
This Network+ online training has additional information about syslog port 514, as well as other common ports and protocols you'll need to know as a network administrator.