What is Port 161?
by Colin Cohen | Published on October 20, 2023

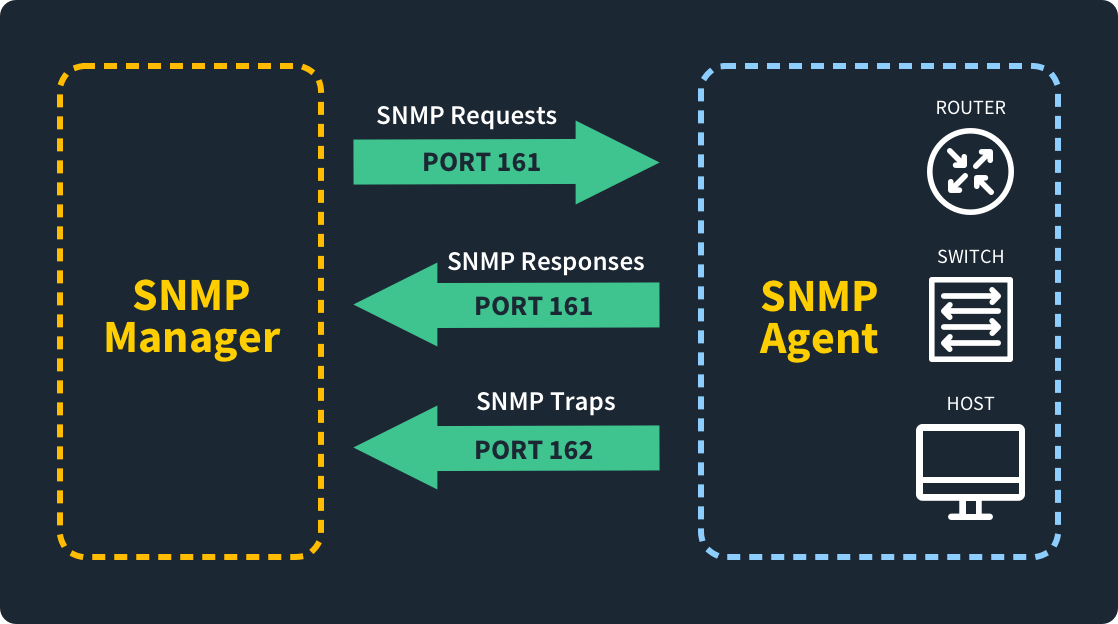
Port 161 is dedicated to the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), which you use to manage and monitor network devices remotely. SNMP managers use port 161 to send commands to the SNMP agents on the devices.
Simple Network Management Protocol Explained
In large, complex networks, you can’t always be in front of the devices you need to manage and monitor. SNMP allows you to do this remotely. It works through communication between SNMP managers and agents. An SNMP manager is a device from which you are managing the network while SNMP agents reside on the network devices that you are managing.
You use port 161 to send commands from the SNMP manager to the SNMP agent. When the SNMP agent needs to communicate back to the SNMP manager, it does this through port 162.
One of the benefits of using SNMP is that it's hardware and software-independent. No matter what kinds of devices are on your network or what operating systems they are running, you can use SNMP.
SNMP Protocol Port 161 and Processing Management Requests
Remote network management applications allow you to manage and monitor your network devices wherever they are. If you want information about a particular device, the application will send an SNMP command to the SNMP agent residing on the device over port 161.
Is SNMP Port 161 UDP or TCP?
You can use either UDP or TCP transport protocol when sending SNMP commands from an SNMP manager to an SNMP agent over port 161. In practice, though, you will typically use UDP. This is because SNMP data usually doesn’t require the overhead associated with TCP, and using UDP is faster.
What is Port 161 Used For?
Many leading network management and monitoring applications use port 161 to send SNMP commands to remote devices.
Gathering Information and Monitoring Network Devices with SNMP Port 161
Managing network health is a critical task for network administrators. They need to monitor many network devices from a central location.
To do this, they use SNMP-based network managing and monitoring applications to constantly gather information about their devices over port 161 so they can prevent service interruptions.
Configuring and Managing Devices with Port 161
For large organizations, it is impossible for network administrators to physically manage and configure each device in their network. Instead, they use applications that communicate to their devices remotely using SNMP over port 161.
Network Management Software Depends on SNMP 161
Many leading network management and monitoring applications use SNMP by sending commands to network devices over port 161.
These applications include the following:
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
ManageEngine OpManager
Paessler PRTG Network Monitor
Port 161 Vulnerabilities and Security Concerns
There are serious vulnerability concerns relating to using SNMP over port 161, which you can mitigate by using the latest version of the protocol and blocking the port in your firewall when you don’t need it open.
Successful Attacks Against Port 161
Versions one and two of SNMP are very vulnerable to attacks, as SNMP messages in these protocol versions are sent unencrypted. This allows hackers to read sensitive data, such as credentials, by using a packet sniffer.
Version three of the protocol — which is known as SNMPv3 — provides far better security by adding features such as encryption, authentication, and access control. However, it is important to note that this doesn’t make it impervious to attack. The only sure-fire way to do this is by blocking port 161 in your firewall.
Preventing Weak Authentication With SNMP
Versions one and two of SNMP provide no authentication. But even in version three, you can have weak authentication. You can prevent this by requiring the use of strong community strings that are at least 20 characters in length.
Is Port 161 Safe to Open?
To make your SNMP implementation as secure as possible, you should block port 161 in your firewall. If you absolutely need the port open, you should use version three of the protocol and require strong authentication.
What is the Most Current Version of SNMP?
The most current version of SNMP is version 3, and you should use this to make your SNMP implementation as secure as possible. This primer to SNMPv3 can help you configure it on Cisco routers, and gain a better understanding of how it works.
That said, if security is not a concern, versions one and two of the protocol are simpler to use and may perform better for your needs.
Port Conflicts and Overlaps with SNMP 161
Only one process can listen on a port at one time. So, if you have conflicts on port 161, you need to configure your SNMP agent to listen on a different port.
How to Configure SNMP 161 to Avoid Overlaps
To avoid conflicts, you can have your SNMP agent listen on a different port than 161. You do this by issuing the following command on the agent:
snmp.set –port
What's the Difference Between SNMP Port 161 vs 162
SNMP managers send commands to SNMP agents on port 161. When the agent wants to send an alert back to the manager in what is known as an SNMP trap, it does so over port 162.
SNMP Managers and SNMP Traps
As a network administrator, you want to receive notification if one of your devices has failed or is in the process of failing. The SNMP agent on the device does this by sending periodic data about its state to the SNMP manager over port 162 through what are called SNMP traps.
Key Takeaways About Using Port 161
Using SNMP over port 161 allows you to effectively manage and monitor devices remotely across your network. It sends commands from your SNMP managers to your SNMP agents over the port. When your agents need to communicate back to the managers, they do so over port 162.